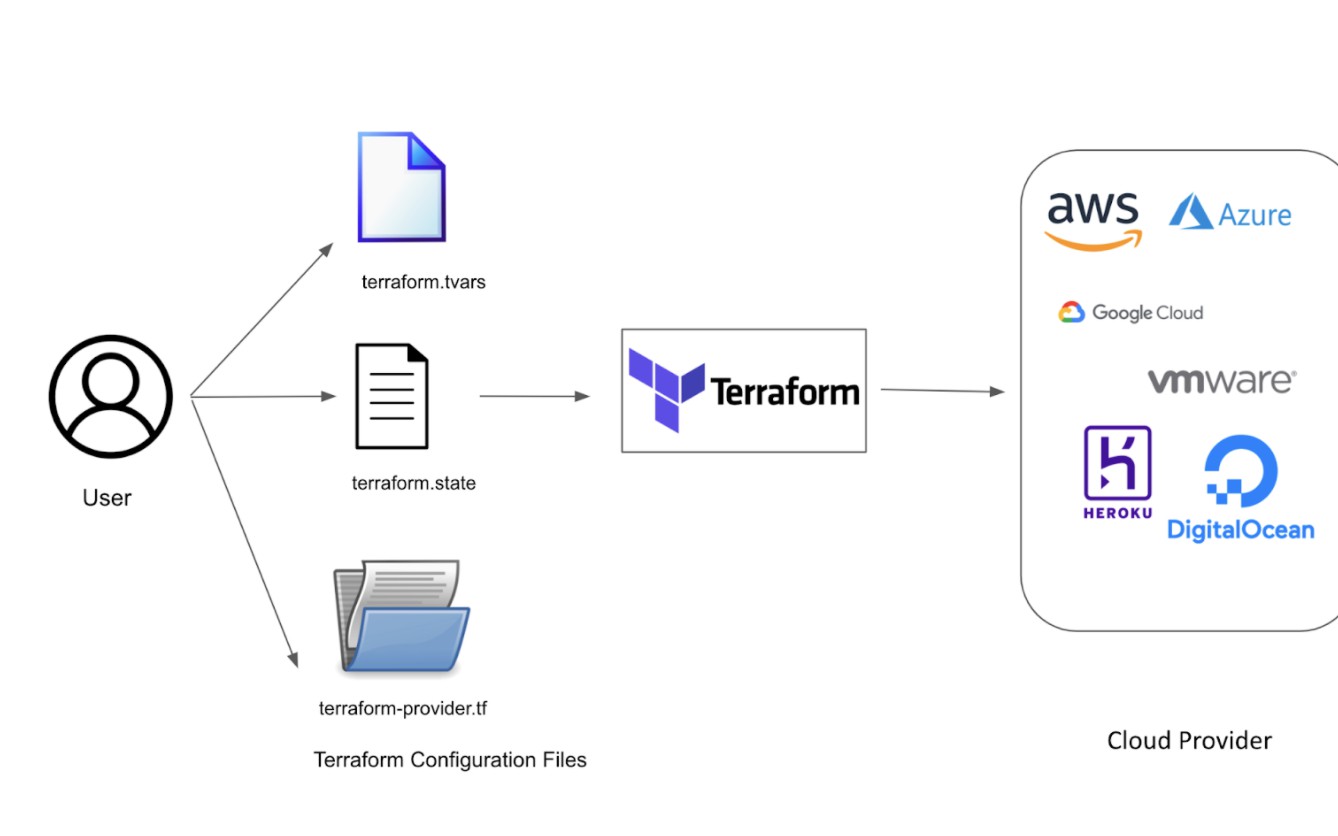
One widely used Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tool that simplifies the deployment and upkeep of complex systems is Terraform. It allows infrastructure resources to be managed via code. In order to specify the desired state of the infrastructure, declarative configuration files, usually written in HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL), are the foundation of Terraform. These files, which are frequently called .tf, are configuration files that hold information about providers, resources, variables, and outputs. They act as blueprints for the system components. The cloud or service provider where the resources will be provisioned is specified by providers in Terraform configuration files. From well-known cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud to specialized services like GitHub or Kubernetes, providers offer a variety of services. Every provider is listed in the configuration file, along with any configuration parameters required to communicate with the target environment and authentication information.
The discrete infrastructure elements that Terraform oversees are referred to as resources. Virtual machines, databases, networking components, and other items may be among them. The type, name, and any necessary properties of each resource are defined in the configuration file. To define an AWS EC2 instance, for instance, you would need to provide the instance type, AMI, and networking information. Terraform configurations can be parameterized through variables, which enable the passing of dynamic values into the definition of the infrastructure. It is possible to define variables externally via variable files or environment variables, or internally within the configuration file itself. The adaptability of this allows deployments to be customized without changing the underlying code and configurations to be reused across environments. After the infrastructure has been provisioned, Terraform can reveal specific values by using outputs. These could consist of DNS names, IP addresses, or any other pertinent data. The configuration file contains declarations for outputs, which are useful for post-deployment activities like configuration management or updating other systems on the status of the infrastructure.
Terraform configurations can be contained and reused with the help of modules. Code reuse and maintainability are encouraged by modules, which are self-contained packages of Terraform configurations that can be called repeatedly with various inputs. In order to promote a modular approach to infrastructure management and abstract away complexity, modules can represent a single resource or a group of related resources. Terraform configuration files adhere to a particular syntax that is specified by the HCL language. Infrastructure configurations can be represented succinctly and clearly with this human-readable syntax. Furthermore, Terraform allows advanced configuration logic to be expressed within the files by supporting features like conditionals, loops, and functions.
Configuration files for Terraform must include versioning and state management. The infrastructure that is controlled by the configuration files is tracked by Terraform in a state file that is updated dynamically. To guarantee that Terraform can precisely identify the steps required to reach the desired state, this state file is used to plan and implement changes. Terraform configurations are frequently managed with version control systems such as Git, which offer a history of changes and let team members collaborate more easily.
Configuration files for Terraform offer a robust way to define and manage infrastructure as code. Through the use of declarative syntax, variables, outputs, modules, and versioning mechanisms, Terraform makes it possible to automate infrastructure provisioning and maintenance, which results in deployment workflows that are more scalable and effective, with the file extensions.tf and .tf.json, configuration files are a collection of files used in Terraform to describe infrastructure. Infrastructure is defined using a declarative model by Terraform. You can write a configuration file that declares the state you want to be in. Configuration files consist of resources that have values and settings that indicate how you want your infrastructure to be.
